Telnet (en)
Telnet (Telecommunication Network) is a protocol to access remote computers using Unix or Linux operating systems. The telnet-protocol uses a network connection from the client computer (like a Windows or a Linux PC) to the server computer. In most cases here the server is the Dreambox receiver. The goal of a telnet session is to operate the server at the shell.
Because the transmission is in plain text, passwords can be captured by simple methods. You should use encrypted protocols like SSH.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Clientsoftware
A Telnet client is installed on nearly every computer. In Windows, you do it generally via the command line. In Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8, the telnet client must be enabled first. In Linux, simply use the telnet command from the shell. You can also use other programs to connect to a Telnet server.
Attention: Some clients need a password that must first be set via telnet (e.g. SSH will not work without a password).
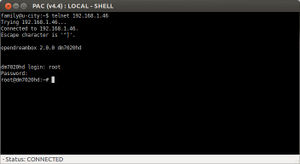
Start Session
The call is made in each case from the console with
telnet $IP_Addresswhere $IP_Address is of course the IP address of your Dreambox (e.g. 192.168.0.1).
The presets on the boxes are: on DM500, DM5600, DM5620, Triax 272, DM7000
- username: root
- password: dreambox
on DM 500+, DM 500 HD (v2), DM 520, DM 600 PVR, DM 520, DM 525, DM 800 HD PVR, DM 800 HD se (v2), DM 820 HD, DM 900, DM 920, DM 7020, DM 7025(+), DM 8000 HD PVR, DM 7020 HD (v2), DM 7080 HD
- username: root
- no password
After logging in, you are at the Linux shell.
Password
Use the following article to set or change the password.
 see article: Change password via telnet
see article: Change password via telnet see article: Set password protection via Blue Panel
see article: Set password protection via Blue Panel
Commands in the Shell
Read the overview about BusyBox.
"Telnet" is usually running in command-lines.
The equivalent in Windows is the "DOS window" or the "Command line".
In Linux, it is e.g. Shell, Bash, Terminal and so on.
More information about Telnet is available on Wikipedia.