GP3.2 OpenVPN (en): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Mfgeg (Diskussion | Beiträge) K |
|||
| Zeile 338: | Zeile 338: | ||
If you need help with OpenVPN, follow the link ;) | If you need help with OpenVPN, follow the link ;) | ||
| − | geminiopenvpn | + | [http://www.i-have-a-dreambox.com/wbb2/thread.php?threadid=172937 geminiopenvpn (ihaD)] |
'''Back to overview: [[Gemini-Wiki:English Portal]] or [[Mainpage]]''' | '''Back to overview: [[Gemini-Wiki:English Portal]] or [[Mainpage]]''' | ||
Version vom 17. September 2012, 18:56 Uhr
InhaltsverzeichnisAfter installing the geminiopenvpn Plugin you have an OpenVPN Server or Client which is easy to configure. The plugin uses certificates (Server-Multi-Client). The connection on the OpenVPN Server is made over an encrypted TLS connection. For connections the OpenVPN Server Plugin creates a virtual network interface (tap0), which is connected over a network bridge (br0) with the internal network adapter (eth0) of the Dreambox. One or more OpenVPN clients get an IP address of the internal network and can access all available services without additional routing. The mode used by OpenVPN is Bridging. With this mode the Broadcasts are forwarded without any problem. Same for network protocols like IPv4, IPv6, Netalk, IPX, ...
Requirements for using OpenVPN
OpenVPN ServerInstall the OpenVPN Plugin via BluePanel and configure the Server as described. After rebooting you find the OpenVPN Server (and client) in the BluePanel. It's also possible to install the plguin over the console with the following command: opkg update && opkg install geminiopenvpn
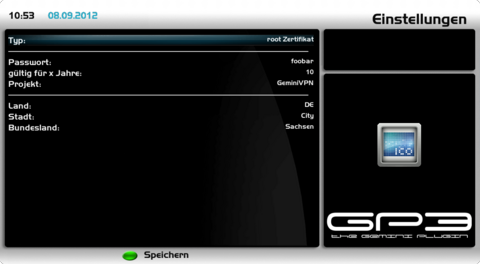
Create Root CertificateNow we create the keys and certificates for the Certificate Authority (CA). Open the OpenVPN Server Plugin and push the [green] button for certificates. Choose root-certificate and change the settings as described in the list. For all parameters only letters and numbers can be used.
Save the settings with the [green] button. The corresponding files will be created and saved in the directory /etc/ssl/openvpn.
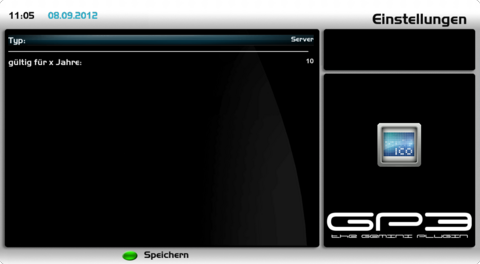
Create Server CertificateOpen the OpenVPN Server Plugin and push the [green] button for certificates. Push again the [green] button and choose as type the setting Server and change the settings as described in the list.
Save the settings with the [green] button to create the certificates. You will be prompted to enter the password (which was entered while creating the root certificate). When a wrong password is entered the following error message is displayed: can't generate certificate. When the correct password is entered the certificates, keys and the Diffie-Hellman parameters are created. This can take some minutes (up to 30 min), the status is displayed in the plugin. The plugin can be closed while the creation is in progress, the process continues in background.
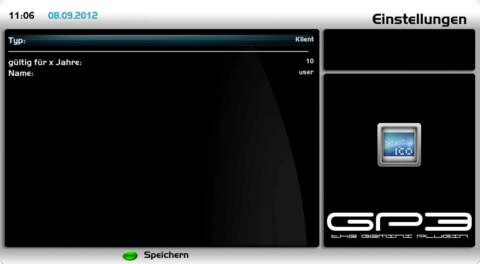
Create Client Certificate(s)Open the OpenVPN Server Plugin and push the [green] button for certificates. Push again the [green] button and choose as type the setting Client and change the settings as described in the list.
Save the settings with the [green] button to create the certificates. You will be prompted to enter the password (which was entered while creating the root certificate). When a wrong password is entered the following error message is displayed: can't generate certificate. When the correct password is entered the client certificate, key and configuration file can be found in the following directory: /etc/ssl/openvpn These files (three files for each client) will be used later on the OpenVPN clients to set up a connection with the server. The needed files look like follows, e.g. if the entered name was 7020hd. In addition to the three files every client needs the Root Certificate (vpn-ca.pem).
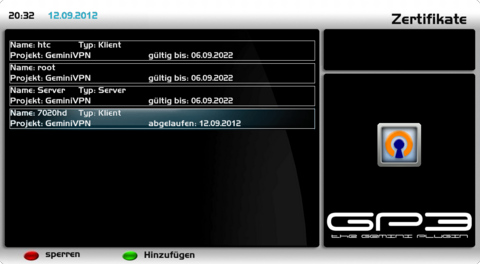
Overview of the configurationThe created configurations can be displayed with the [green] button (certificates) in the OpenVPN Server Plugin. The example shows the configuration for a root certificate, Server settings and the configuration of two clients, with the names htc and 7020hd.
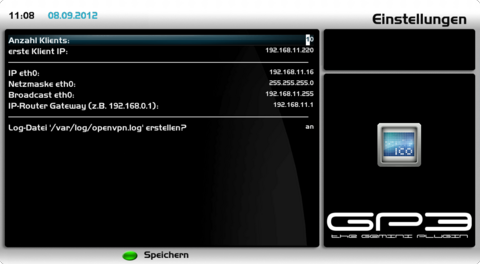
SettingsOpen the OpenVPN Server Plugin in the BluePanel under the daemons. Now we check first the settings, before starting the OpenVPN Server. Push the [blue] button and choose the point [Settings]. Use the following list for the descriptions and modify if requires. The network settings should be taken from the Dreambox and should only be changed in rare occasions.
Save the settings with the [green] button. After saving the settings the OpenVPN Server is started automatically. The OpenVPN Server will also be started automatically after restarting the Dreambox, when a configuration file and certificates are available.
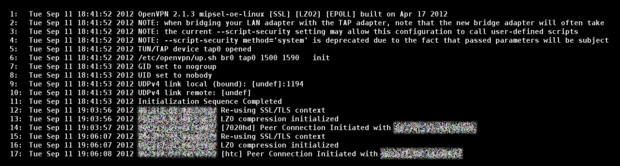
OpenVPN Log FileInformations about the status of the OpenVPN server can be displayed with the [red] button (Log file). The example shows the OpenVPN server was started successful with two connected clients. The log file can also be displayed in the terminal with the following command: cat /var/log/openvpn.log
Overview of connectionsThe OpenVPN Server Plugin controls regularly if clients are connected and shows the connections as in the image Active connections. In this example two clients are connected, with the name htc and 7020hd.
Block certificate(s)Certificates can be blocked, when you want to deny access from a client. Blocking is done over the [red] button, when the menu of the certificates is opened. Blocked client certificates are displayed as expired. For blocking the correct password (which was used for creating the root certificate) needs to be entered.
OpenVPN Server - Menu buttonOpen the OpenVPN Server Plugin and push the [blue] button of the remote control. The functions are described in the following list.
Delete certificatesCertificates can not be deleted in the OpenVPN Server Plugin. The files need to be deleted manually in the directory: /etc/openvpn/ssl
OpenVPN ClientThere are many different OpenVPN Frontends, for different operation systems, to connect with a OpenVPN Server. The following points describe the configuration of the OpenVPN client on a Dreambox (with the GP3.2 Plugin) and an Android based Smartphone.
Dreambox as clientWhen configuring the OpenVPN clients you need to copy the 4 files created on the server before in the directory of the client: /etc/openvpn Once more the list of the required 4 files for the OpenVPN client. The xxx stands for the name which was given for the client.
Edit configuration fileBefore setting up a connection the configuration file (*.ovpn) needs to be edited. The line remote needs to be completed with the IP address or the host address and the correct port. the configuration could be similar to the example, when the access uses the host name webaccess.dyndns.tv via port 1194. .
.
# example 'remote foobar.org 1194'
# example 'remote 97.123.100.236 1194'
remote webaccess.dyndns.tv 1194
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
.
.
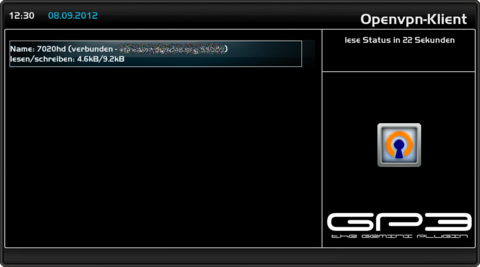
Make connectionOpen the OpenVPN Client Plugin in the BluePanel under Daemons. In the Plugin a line (not connected) appears, when the configuration files were copied in the correct directory (/etc/openvpn). Start the connection with the OpenVPN Server with the [OK] button. If everything starts the status connected is displayed in the OpenVPN Client Plugin. Disconnecting is possible by pressing the [OK] button again.
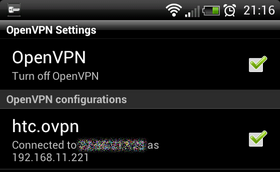
Android Smartphone as clientThe image shows an example of an Android based Smartphone, which is connected with the Dreambox. As App is used OpenVPN settings to connect with the Server. Keep in mind the Smartphone needs to be rooted to use OpenVPN. Additional the tun/tap driver, the Busybox and OpenVPN is required. With many Custom-Roms these requirements are already integrated in the Firmware. The config file (*.opvn) needs to be edited with the correct server and port. Copy the client files on the SD card, e.g. in a directory openvpn. Now you need to adapt the OpenVPN App (e.g. path to the configuration, certificates) and the tunnel on the OpenVPN Server can be started.
Support threadIf you need help with OpenVPN, follow the link ;)
|