BusyBox (en): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Mfgeg (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Mfgeg (Diskussion | Beiträge) K (Mfgeg verschob Seite Busybox (en) nach BusyBox (en) ohne dabei eine Weiterleitung anzulegen) |
(kein Unterschied)
| |
Version vom 6. November 2013, 21:12 Uhr
This article is about the basics of the Busybox and the most used commands. Feel free to add new commands...
Inhaltsverzeichnis
BusyBox
The Busybox includes all known commands of the Dreambox.
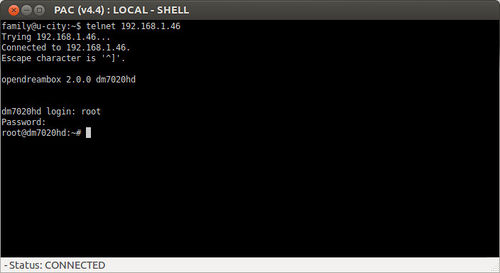
To have a closer look at them, first connect via Telnet, as described in chapter Telnet
Start Telnet, which may look like that:
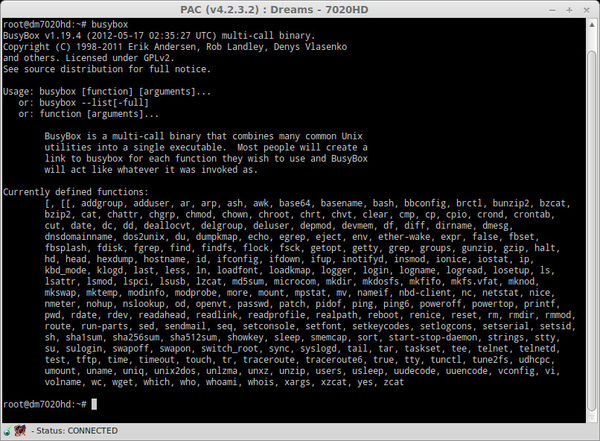
Here we use the command "busybox", which gives us
all known Linux commands, which are supported by the Dreambox.
Commands - what is the found command good for?
The purpose or usage of a command can easily be found out by using the
option "-h" or "-help"
If you are stuck and the shell is frozen, simply use Ctrl + c to exit
The command "chmod -help" for instance leads to:
root@dm800:~# chmod -help BusyBox v1.01 (2008.11.26-20:45+0000) multi-call binary Usage: chmod [-R] MODE[,MODE]... FILE... Each MODE is one or more of the letters ugoa, one of the symbols +-= and one or more of the letters rwxst. Options: -R Changes files and directories recursively.
The command "grep -h" for instance leads to:
root@dm800:~# grep -h BusyBox v1.01 (2008.11.26-20:45+0000) multi-call binary Usage: grep [-ihHnqvs] PATTERN [FILEs...] Search for PATTERN in each FILE or standard input. Options: -H prefix output lines with filename where match was found -h suppress the prefixing filename on output -i ignore case distinctions -l list names of files that match -n print line number with output lines -q be quiet. Returns 0 if result was found, 1 otherwise -v select non-matching lines -s suppress file open/read error messages
Important shell commands
passwd
passwd changes the passwords for user- and group accounts. A normaluser may only change his password, a superuser max change the passwords of all accounts. The administrator of a group may change the password of this group. passwd may also change the accountinformation like comment, loginshell or password-lease-time and -intervall
init 4
init 4 may change the runlevel. By calling this command init sends a stopsignal to all processes who are not defined for the new runlevel. After that the processes are "killed" and the processes for the new runlevel, who are not running yet are started. This command is especially useful at Enigma2 boxes
when system has crashed or hung up or we'd like to know something about the actions of the Enigma2 system.
init 3
init 3 restarts Enigma2 after init 4.
enigma2
enigma2 also restarts the enigma2 like init 3 after init 4 but you can follow each step in the shell and find errors easier.
More commands
cat: is used for view files and its content
(e.g.: cat /etc/resolv.conf)
cp: is used for copying files at the box.
(e.g.: cp /tmp/DATEINAME /etc/)
First name origin directory, then name target directory.
mv: means "move" and is used for moving / renaming
(e.g.: mv /etc/TESTNAME /etc/TESTNAME_NEU)
fdisk: partitioning program
mkfs: is used for formatting
fsck: command for file system checks
chmod: change of data attributes (access rights).
(e.g.: chmod 755 /usr/bin/mc).
Command makes the file mc executable.
mc: is a file manager, who is already installed on the Dreambox.
free: see memory usage (RAM)
df -h: see memory usage (storage devices)
find . | grep FILENAME: command for finding a file
Continuative links and information
More information and usage examples about the shell commands max be found at
different Dreamboxboards or Linuxboards or Wikis, HowTo`s and books.
Here a Link to the IHAD board to a PDF with a summary of different linux commands
[1]
as well as a link for simple Unix commands
[2]