Automount (en)
The Automounter is a service (consisting of automount/autofs), to mount file systems automatically. Mounting is performaed when accessing the configured directories. Unmounting is performed by default after 5 sec. of inactivity (depending on the used image). On dreamboxes the service is used to access network shares. The shares can be accessed over cifs and/or nfs.
After mounting the share it's possible to play supported movies, music and images. The network shares can be on Dreamboxes, Linuxr computers, Macs, NAS and Windows computers.
Advantage of the automounter: no scripts, editing of the fstab or boot settings are required.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Functionality Automounter
For the preamble Automount Mounter, two files are important, autofs and automount. Autofs defines the mount points using the auto.master file. Afterwards the mounting is performed by automount.
Goal of the article
- Learn the configuration of the Auto Mounter
Prerequisites
- Knowing the BluePanel (Automount - Editor) and the remote control
- Editing the configuration file with an unix compatible editor
Configuring the Automounter
There are 3 ways to configure the automounter.
- The Automount Editor of the BluePanel
- Or editing the configuration file
- With the GP3 Plugin and the installed Netscan Plugin, Samba and NFS shares can be found and passed to the Automount Editor.
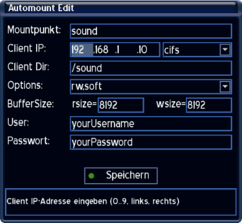
Configuration via Automount Editor
The Automount Editor is available in Enigma since Gemini Project 1.9 and in Enigma2 since Gemini Project 3.2 in the BluePanel.
- With Enigma (since version 4.5) the Automount-Editor can be found in the BluePanel under Extras / Settings => Automount
- With Enigma2 (since version 4.1) under Settings => Automount Editor
- With the installed GP3 Plugin under BluePanel => Settings => Automount Editor
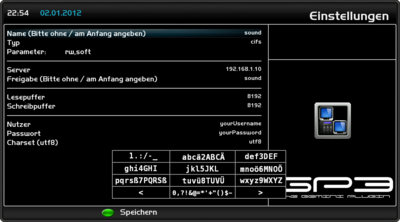
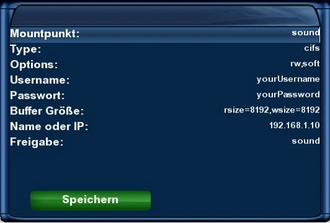
Example CIFS Mount
Example of a cifs mount.
The settings need to be changed according to your situation.
description of the settings
Name
Enter the name of the device (e.g. sound). The autofs daemon creates a directory with the selected name.
The path of the directory is saved in the file auto.master.
Read: Accessing the mount point.
Attention: if using multiple mounts, the name (mount point) should always be different.
Typ
selection of the protocol CIFS.
Parameter
Options for the mount.
Server
IP address of the source device.
Share
Enter the name of the shared directory.
Attention, with Enigma2 there schouldn't be a / (Slash) entered at the beginning!
read / write buffer
The options rsize and wsize define the size of the data packages, which are exchanged by the client and server.
User
Enter the user name of for the access on the source device.
Password
Enter the password for the access on the spurce device.
Charset (utf8)
Sets the character encoding onto utf8, useful for special characters.
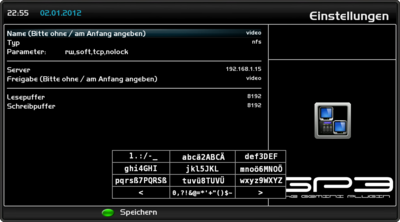
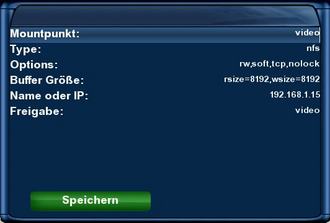
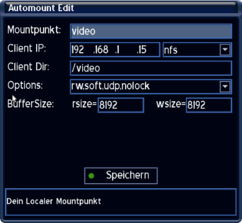
Example NFS Mount
Example of a nfs mount.
The settings need to be changed according to your situation.
description of the settings
Name
Enter the name of the device (e.g. sound). The autofs daemon creates a directory with the selected name.
The path of the directory is saved in the file auto.master.
Read: Accessing the mount point.
Attention: if using multiple mounts, the name (mount point) should always be different.
Typ
selection of the protocol NFS.
Parameter
Options for the mount.
Server
IP address of the source device.
Share
Enter the name of the shared directory.
Attention, with Enigma2 there schouldn't be a / (Slash) entered at the beginning!
read / write buffer
The options rsize and wsize define the size of the data packages, which are exchanged by the client and server.
Accessing the mount point
The access of the created mount point depends on the Gemini version. The easiest way is to use the File Mode (Enigma), or the File Manager (Enigma2).
- For Enigma boxes the mount point can be found in the directory /automount.
- For Enigma2 up to GP version 3.8 the mount point is in /automount. From version 3.9 till 4.1 it can be found in /autofs. And from 4.2 upwards in /media/net.
Configuration via configuration file
The configuration file of the automounter for CVS Boxes can be found in /var/etc and for OE Boxes in /etc (CVS/OE Boxes see here). Here you can find also the different fiels depending on the image version. The syntax remained the same.
- With Enigma the file name is automount.conf. The configuration is possible since Gemini Project 3.1.
- With Enigma2 the file name is automount.conf for Gemini Project 1.8 - 3.8. Since version 3.9 - 4.1 the file name is auto.hotplug. And from version 4.2 upwards the name is auto.network.
| The permissions with OE 2.0 images should be 644. The file shouldn't be executable! You can change the permission with the command chmod 644 /etc/auto.network. |
| After the creation of a mount point, the Box or the autofs daemon should be restarted. |
Example CIFS mount
Example of a cifs mount.
The settings need to be changed according to your situation.
sound -fstype=cifs,rw,soft,rsize=8192,wsize=8192,iocharset=utf8,user=Benutzername,pass=Passwort ://192.168.1.10/sound
description of the settings
Name
Enter the name of the device (e.g. sound). The autofs daemon creates a directory with the selected name.
The path of the directory is saved in the file auto.master.
Read: Accessing the mount point.
Attention: if using multiple mounts, the name (mount point) should always be different.
-fstype=
selection of the protocol CIFS.
rw,soft
Options for the mount.
user=user_name
Enter the user name of for the access on the source device.
pass=password
Enter the password for the access on the spurce device.
rsize=8192,wsize=8192
The options rsize and wsize define the size of the data packages, which are exchanged by the client and server.
iocharset=utf8
Sets the character encoding onto utf8, useful for special characters.
://192.168.1.10
IP address of the source device.
/sound
Enter the name of the shared directory.
Attention, with Enigma2 there schouldn't be a / (Slash) entered at the beginning!
Example NFS mount
Example of a nfs mount.
The settings need to be changed according to your situation.
video -fstype=nfs,rw,soft,tcp,nolock,rsize=8192,wsize=8192 192.168.1.15:/video
Beschreibung der Angaben
video
Namen des Zielgerätes (z.B. video) eingeben. Der autofs Dienst legt automatisch ein Verzeichnis mit dem Mountpunktnamen an.
Der Pfad zu dem Verzeichnis ist in der Datei auto.master definiert.
Lest dazu den Abschnitt Zugriff auf den Mountpunkt.
Achtung: Werden mehrere Mounts auf Freigaben eingerichtet, dann muss der Mountpunktname immer unterschiedlich sein.
-fstype=
Auswahl des Protokolls NFS.
rw,soft,tcp,nolock
Optionen für den mount.
rsize=8192,wsize=8192
Die Optionen rsize und wsize bestimmen die Grösse der Datenpakete, welche Client und Server austauschen. Die Angaben sind je nach Gerät verschieden. Falsche Angaben verlangsamen den Zugriff!
192.168.1.15:
IP Adresse des Zielgerätes eingeben.
/video
Pfad der Freigabe eintragen.
Accessing the mount point
The access of the created mount point depends on the Gemini version. The easiest way is to use the File Mode (Enigma), or the File Manager (Enigma2).
- For Enigma boxes the mount point can be found in the directory /automount.
- For Enigma2 up to GP version 3.8 the mount point is in /automount. From version 3.9 till 4.1 it can be found in /autofs. And from 4.2 upwards in /media/net.
Interessante Shell Befehle für den Automounter
| Unter Enigma bietet der Automounter die Optionen {start|stop|restart}. Das Script heisst autofs_script.sh |
Beispiele einer Enigma2 basierenden Dreambox
Stoppen von autofs
/etc/init.d/autofs stop
Starten von autofs
/etc/init.d/autofs start
Neustarten von autofs
/etc/init.d/autofs restart
Änderungen einlesen der Konfigurationsdatei
/etc/init.d/autofs reload
Status Abfrage
/etc/init.d/autofs status