GP3 Netscan (en)
The gemininetscan Plugin scans the local network for available devices with fping. Subsequently a port scan can be performed to discover shares (with amap) or open Ports. The result is displayed on the TV screen. Following functions are covered by the plugin:
- Scan the local network for available devices (via eth0 or wlan0).
- Executes a port scan for the discovered devices.
- Display the MAC addresses of the devices, including the manufacturer info.
- Scans for available Samba, NFS and FTPshares.
- Can transfer the found shares directly to the Automount Editor.
- Supports WOL, to wake up devices.
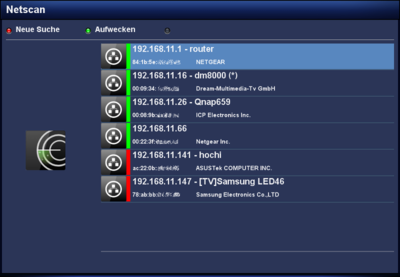
- Displays active / inactive devices (
 = online /
= online /  = offline).
= offline).
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Installation / Deinstallation
The gemininetscan plugin can be installed / removed in different ways:
 see article: GP3 Addons - Category: Gemini Plugins
see article: GP3 Addons - Category: Gemini Plugins see article: WebAdmin - Package name:
see article: WebAdmin - Package name: gemininetscan see article: APT - Package name:
see article: APT - Package name: gemininetscan see article: OPKG - Package name:
see article: OPKG - Package name: gemininetscan
Restart Enigma2 after the installation, or reboot the Dreambox.
Operation
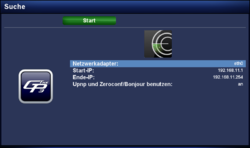
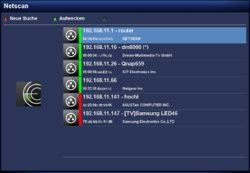
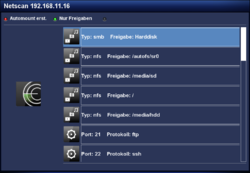
After starting the plugin, you can open the settings with the red button. The following table lists the different options. The scan can be started with the Start button. Once the scan of the network is completed, a list of available devices is displayed. Including the informations concerning the manufacturer, MAC addresses, .... An additional scan can be started at any moment over the red button.
| Entry | Description |
|---|---|
| Network interface: | Selection of the network interface e.g. eth0 or wlan0, which will be used for the scan (if multiple interfaces are available). |
| Start IP: / End IP: | Range or IP addresses for the scan. |
| Use Upnp and Zerokonf/Bonjour: | If the setting is on, the devices are searched via Upnp/Avahi. Use off if the search initiates a router crash (e.g. Fritzbox). In this case the search is performed via DNS functions (nslookup) and Samba. |
Start portscan
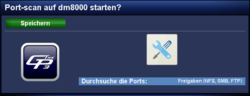
A portscan for the found devices can be executed. Select the wanted device with the OK button. In the following window, it is possible to perform a scan for the device with the following settings (see below). Use the navigation buttons ◀ ▶, to change the settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Shares (NFS, SMB, FTP): | Search only for NFS, SMB and FTP shares. Keep in mind, SMB shares from Windows XP upwards are not displayed. |
| Standard: | Search for available services and shares |
| 1-1023: | Search for standard ports (well known ports). |
| 1-49151: | Search for standard ports and registered ports. |
| 1-65535: | Scan complete port range (standard, registered and dynamic). |
After the selection is made, the portscan can be started with Save, or the OK button. After the search is finished, the found info (services, shares) are displayed on the screen.
After the portscan is completed, the found SMB or NFS shares are identified with the text Share:. It's possible to use a filter with the green button (only shares). This will only display the found NFS and SMB shares. Use the green button (show all) again, to see all informations.
Keep in mind, the WinXP shares will not be displayed, only the pure NFS and Samba Server shares.
Mounting a NFS or SMB share is easy. Select the share and push the red button. The share will be transfered to the Automount Editor. Modify the settings and the device can be reached over /media/net/mountpoint.
Wake up
Wake up of devices is performed in the list with the green button. Keep in mind, the devices should support WOL and the function needs to be activated. Please read the manual of your used devices. To wake up devices, the /usr/bin/ether-wake command of BusyBox is used.
Configuration file
The informations of the scanned network is stored in the JSON file gnetscan.json in the Gemini Cache.
Scan via Terminal
It's also possible to scan the network via Telnet (en) or SSH, e.g. for testing purposes. Use your IP range, the used interface (e.g. eth0, wlan0, br0, ...). The command is:
gnetscan -d eth0 -f 192.168.1.1 -l 192.168.1.254 -o '/home/root/.geminicache/gnetscan.json'